https://ift.tt/soQRiec Data science continues to be a vital field, driving innovation across industries. Even with the tech layoffs of 202...
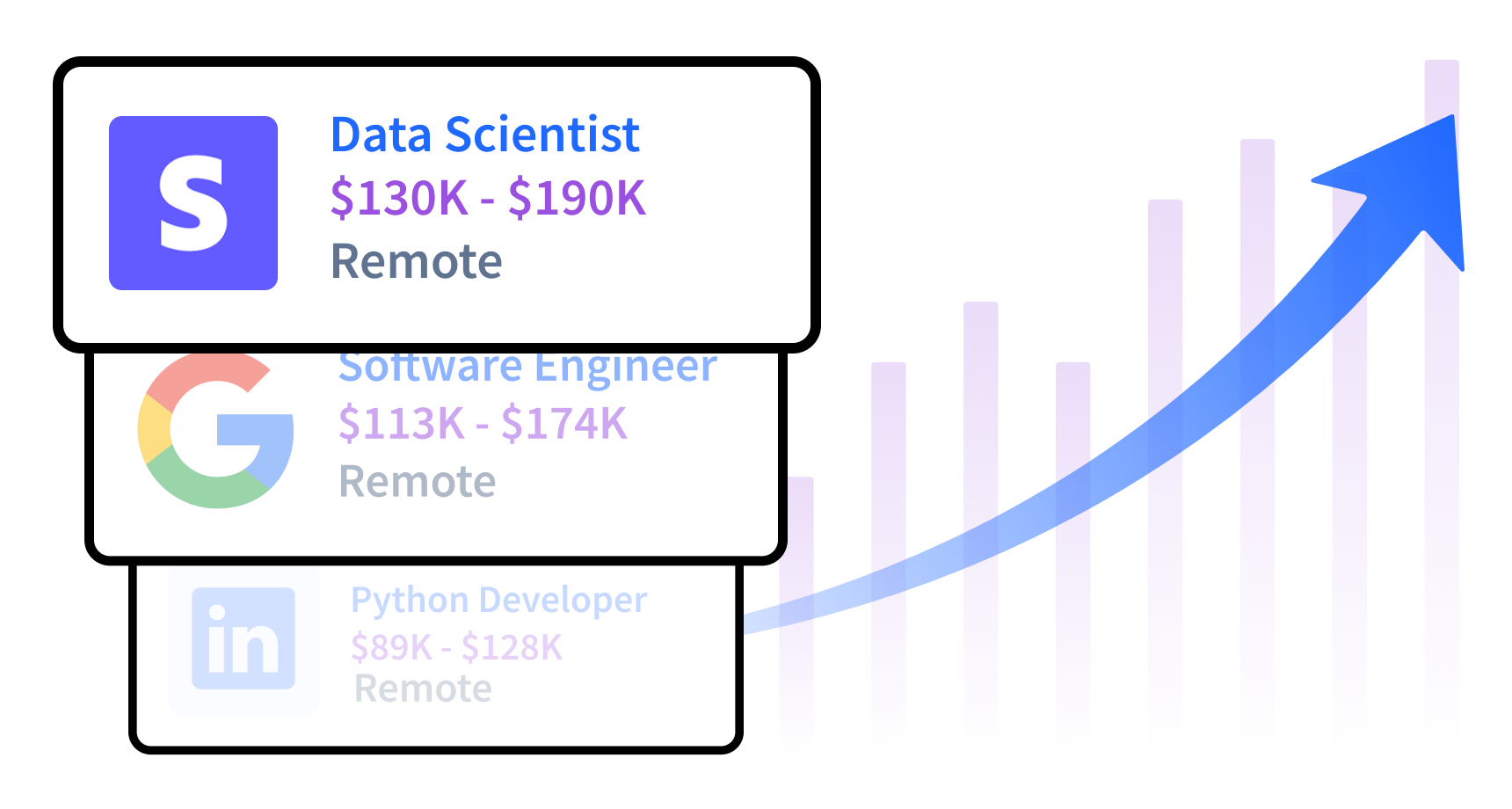
Data science continues to be a vital field, driving innovation across industries. Even with the tech layoffs of 2023, data science jobs were largely spared, highlighting their importance to business growth.
Impact of AI and Automation on Job Demand
The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 finds that emerging technologies will create many more jobs than they cut. About 170 million new jobs are projected globally by 2030 due to tech adoption, even as ~92 million roles are displaced―a net +78 million increase in employment.
In the same report, the WEF forecasts that AI and data processing trends will create 11 million new jobs by 2030 and replace about 9 million, still yielding a net gain of jobs overall. In other words, the AI revolution is set to add jobs on balance, even as certain tasks become automated.
Why Choose a Career in Data Science?
Pursuing a data science career offers major advantages, including strong job security, room for advancement, and the chance to make a real impact across industries.
If you're thinking about a career in data science, here are three solid reasons it's a smart move:
- Job Security: According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, data scientist employment is projected to grow by 36% from 2023 to 2033, significantly outpacing the average growth for all occupations.
- Growth Opportunities: Data science is constantly evolving, providing ongoing opportunities to learn, grow your skills, and advance your career as technology progresses.
- Meaningful Impact: As a data scientist, you can use your skills to drive key decisions and innovations that shape an organization's future.
These advantages make data science more than just a job―it's a path to a rewarding long-term career that stays relevant as the world and technology change.
In short, a data science career offers strong job prospects, significant room for professional development, and the opportunity to do impactful work across many fields.
So What Exactly Does a Data Scientist Do?
Basically, they tackle more advanced analysis than data analysts, build predictive models and apply sopthisticated techniques to improve outcomes. This article will walk you through some of the most promising data science jobs, detailing specific responsibilities, salary ranges, and must-have skills for each role. By the end, you'll:
- Discover 10 in-demand data science jobs
- Understand key responsibilities, salary ranges, and skills for each position
- Get tips for gaining practical experience to advance your career
Whether you're looking to become a data analyst or level up to a data scientist position, understanding the nuances of these different data roles will help you chart the right course. We'll cover the key details of each one, and how to gain the practical skills that can take your career to new heights.
Let's get started!
Top 10 Data Science Jobs
Here are the top 10 data science jobs that are currently shaping the industry:
- Data Engineer
- Database Administrator
- Data Architect
- Data Scientist
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Deep Learning Engineer
- Business Intelligence Developer
- Data Translator
- Data Privacy Officer
- AI Engineer
1. Data Engineer
Data engineers are essential for building, maintaining, and optimizing the technical infrastructure that powers data-driven decision-making. While data scientists focus on analyzing data to uncover insights, data engineers work behind the scenes, ensuring data is reliably collected, stored, and accessible to analysts and scientists.
On a typical day, a data engineer might design databases, pull data from APIs, write scripts to transform datasets, build automated pipelines, and manage cloud infrastructure. They collaborate closely with data analysts and scientists to ensure datasets are ready for analysis and reporting.
Salary: \$111K–\$164K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities
- Build scalable data pipelines to transform and process large datasets efficiently.
- Maintain robust databases and data warehouses for easy access and analysis.
- Ensure efficient data collection from APIs and external data sources.
- Develop and automate data workflows using tools like Airflow and dbt.
- Collaborate with stakeholders to understand data needs and provide technical solutions.
Key Skills
- Coding expertise in languages such as Python, Java, or Scala.
- Deep knowledge of SQL and NoSQL databases.
- Hands-on experience with big data frameworks like Hadoop and Apache Spark.
- Cloud infrastructure experience on platforms such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Ability to implement CI/CD pipelines and automated data processes.
As businesses increasingly leverage data, skilled data engineers are vital for enabling robust analytics and machine learning capabilities. Their technical expertise ensures that data infrastructure is reliable, scalable, and accessible to drive informed business decisions.
2. Database Administrator
Database Administrators (DBAs) safeguard an organization's critical data by managing, securing, and optimizing database infrastructure. While data scientists analyze and interpret data for strategic insights, DBAs ensure databases operate smoothly, securely, and efficiently, providing a robust foundation for all data-driven activities.
On a typical day, a DBA might monitor database performance, manage user access and security, and execute backup and recovery plans. They also collaborate closely with IT teams to implement new database systems, fine-tune database queries, and proactively troubleshoot issues to maintain optimal performance.
Salary: \$99K–\$143K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities
- Design, implement, and manage database systems and infrastructures
- Ensure efficient data storage, retrieval, and performance optimization through regular tuning
- Develop and oversee database backup, recovery, and security protocols
- Monitor system performance, proactively identifying and resolving database issues
- Coordinate with technical teams to integrate databases with existing software and infrastructure
- Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA) and internal governance policies
Key Skills
- Proficiency in SQL and relational databases (Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- Familiarity with NoSQL databases (MongoDB, Cassandra) and cloud-based database solutions (AWS, Azure)
- Experience with database optimization techniques and query performance tuning
- Strong analytical thinking and problem-solving skills for identifying and resolving technical issues quickly
- Excellent collaboration and communication skills to work effectively with technical and non-technical stakeholders
Database Administrators are indispensable as organizations increasingly rely on data-driven insights. Their meticulous attention to detail, technical expertise, and proactive maintenance of database infrastructure ensure that critical data remains secure, accessible, and efficient—enabling informed decision-making at all levels.
3. Data Architect
Data architects design and maintain comprehensive frameworks for managing an organization's data effectively. While data scientists analyze data to generate actionable insights, data architects define the overarching strategies and structures to manage data at scale, ensuring long-term usability, quality, and compliance throughout the company.
On a typical day, data architects might develop strategic data management policies, design complex data models, and oversee data governance initiatives. They collaborate with senior stakeholders, IT teams, and data professionals to ensure that data infrastructure aligns with long-term business goals and regulatory requirements.
Salary: \$154K–\$237K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities:
- Develop and implement robust data strategies that support business objectives.
- Create and manage detailed data models to ensure efficient data storage and accessibility.
- Oversee data governance, compliance, and security measures.
- Coordinate with IT teams to select and integrate appropriate data management technologies, such as cloud platforms.
- Maintain data quality and integrity across diverse databases and systems.
Key Skills:
- Expertise in data modeling methodologies, including relational and dimensional modeling.
- Strong proficiency with big data technologies (e.g., Hadoop, Apache Spark) and cloud data services (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Knowledge of data warehousing solutions and modern data architecture best practices.
- Analytical abilities to align complex technical solutions with business needs.
- Deep understanding of data compliance and privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA).
Data architects ensure that organizational data is structured to maximize usability, accuracy, and strategic value. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, their role becomes increasingly critical in shaping a company’s ability to use data effectively and ethically.
4. Data Scientist
Data scientists play a pivotal role in transforming complex data into actionable insights that drive business strategy. Their expertise in statistical analysis and machine learning enables organizations to make informed decisions and stay competitive in a data-driven world.
On a typical day, a data scientist might collect and clean datasets, develop and test predictive models, and present findings to stakeholders. They collaborate with cross-functional teams to ensure that the insights derived from data are effectively integrated into business processes, enhancing efficiency and innovation.
Salary: \$131K–\$212K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities
- Analyze large sets of structured and unstructured data to identify trends and patterns
- Develop predictive models and machine learning algorithms to solve complex business problems
- Collaborate with engineering and product teams to implement data-driven solutions
- Communicate findings and insights to stakeholders through reports and visualizations
Key Skills
- Proficiency in Python, R, and SQL for data analysis and manipulation
- Strong understanding of machine learning algorithms and statistical modeling techniques
- Experience with data visualization tools such as Tableau or Power BI
- Excellent communication skills to convey complex findings to non-technical audiences
By leveraging data-driven insights, data scientists help optimize various aspects of a business, including marketing strategies, product development, and customer service. Their work is essential in driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in today's market.
5. Machine Learning Engineer
If you're fascinated by the potential of machine learning to transform industries, a career as a Machine Learning Engineer could be an excellent fit. While Data Scientists often focus on research and experimentation, Machine Learning Engineers are more concerned with the practical implementation of machine learning solutions, taking theoretical data science models and turning them into production-ready applications.
On a typical day, a Machine Learning Engineer might be working on tasks like integrating external datasets to enhance model performance, building APIs to make models more accessible to end-users, or implementing feature transformations to optimize model accuracy. It's a hands-on role that requires a blend of strong technical skills and creative problem-solving.
Salary: \$135K–\$215K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities:
- Designing and developing efficient, scalable machine learning systems
- Implementing machine learning algorithms to solve real-world problems
- Conducting tests and experiments to monitor and improve model performance
- Optimizing machine learning systems for production environments
Key Skills:
- Proficiency in programming languages like Python and C++
- Deep understanding of popular machine learning frameworks (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch)
- Experience with data structures and algorithms for building efficient models
- Familiarity with cloud platforms that support machine learning operations
As more companies look to leverage machine learning, the demand for skilled Machine Learning Engineers will only continue to grow. If you're ready to tackle complex algorithmic challenges and build intelligent systems that drive smarter decisions, this could be the ideal data science career path to pursue.
6. Deep Learning Engineer
Deep Learning Engineers are the masterminds behind advanced AI systems that can learn and make decisions like humans. While data scientists work with all kinds of data, Deep Learning Engineers focus specifically on building complex models using deep neural networks.
What sets Deep Learning Engineers apart is their expertise in cutting-edge machine learning techniques.
They spend their days constructing sophisticated learning systems, fine-tuning algorithms to perfection, and working with teams to put these AI marvels into action.
Salary: \$118K–\$193K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities:
- Building machine learning models that can recognize images and voices
- Optimizing algorithms so models run faster and better
- Teaming up with data scientists and engineers to launch models
- Always learning about the newest deep learning tech
Key Skills:
- Coding like a pro in Python
- Knowing deep learning tools like TensorFlow and PyTorch inside out
- Understanding the ins and outs of neural networks and algorithms
- Solving tough problems and collaborating with others
In today's AI-powered world, Deep Learning Engineers play a vital role in pushing the boundaries of what machines can do. Their innovative work is essential for building smarter, more capable AI systems that will shape our future.
7. Business Intelligence Developer
Business Intelligence (BI) Developers play a key role in transforming raw data into powerful insights that drive smart business decisions. Rather than predicting the future, they focus on analyzing historical information to clearly show how a company has been performing. By thoroughly examining the data, they uncover actionable insights leaders can use to guide their strategies.
On a typical day, a BI Developer might be found defining requirements for BI tools, creating in-depth reports, or constructing sophisticated data models. It's all about ensuring the data is accurate, well-organized, and ready to inform those critical business choices.
Salary: \$105K–\$154K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities:
- Design and build BI solutions tailored to the company's specific needs
- Maintain high data integrity and reliability across all platforms
- Develop user-friendly BI and analytics tools for easy data access
- Optimize BI tool performance based on user feedback
Key Skills:
- Expertise in BI tools such as Power BI, Tableau, or QlikSense
- Strong command of SQL and database management
- Data modeling abilities to support effective BI solutions
- Skill in translating complex data into clear, concise reports
Ultimately, BI developers are instrumental in harnessing the full potential of a company's data. As more organizations recognize the value of data-informed decision-making, demand for these skills continues to grow. For analytically-minded individuals who want to make a real impact on business success, a career as a BI developer can be highly rewarding.
8. Data Translator
Data Translators play a vital role in helping organizations make data-driven decisions. They bridge the gap between the technical world of data science and the practical needs of the business.
While data scientists focus on building complex analytical models, Data Translators ensure those insights are understood and acted upon. They work closely with both technical teams and business stakeholders to align data projects with strategic goals.
On a typical day, a Data Translator might meet with data scientists to discuss their latest findings, then prepare reports explaining the business implications to non-technical colleagues. They are the link that enables data to power meaningful business decisions.
Salary: \$64K–\$119K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities:
- Align data science and business goals
- Facilitate communication between technical and non-technical teams
- Translate complex data insights into actionable strategies
- Manage end-to-end analytics initiatives to ensure business impact
Key Skills:
- Strong data analysis and interpretation abilities
- Excellent communication and stakeholder management skills
- Proficiency with data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI
Increasingly, as organizations become more data-driven, the demand for skilled Data Translators will continue to rise. These professionals enable companies to maximize the value of their data investments.
9. Data Privacy Officer
Data Privacy Officers (DPOs) are essential in safeguarding an organization's data and ensuring compliance with evolving privacy regulations. While data scientists analyze data for insights, DPOs focus on protecting information and adhering to legal standards.
DPOs possess extensive knowledge of privacy laws and excel at translating complex regulations into actionable policies. They actively monitor data practices, assess privacy risks, and update guidelines to align with changing requirements.
On a typical day, a DPO may review data handling procedures, conduct impact assessments, develop privacy policies, and educate employees on proper data practices. They also respond swiftly to address any data breaches or privacy concerns that arise.
Salary: \$119K–\$194K/yr (Glassdoor)
Responsibilities:
- Develop and implement comprehensive data privacy policies for the organization.
- Ensure compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other relevant privacy laws.
- Conduct regular assessments to identify and mitigate privacy risks.
- Train employees on proper data handling practices.
- Promptly address and resolve data breaches or privacy issues.
Key Skills:
- Deep understanding of national and global privacy regulations.
- Ability to assess risks and identify potential security vulnerabilities.
- Technical expertise to implement data protection measures.
- Strong communication skills to explain legal requirements across the organization.
As reliance on digital data increases, Data Privacy Officers are becoming increasingly critical. They enable organizations to use data ethically while diligently safeguarding individual privacy in a constantly evolving regulatory environment.
10. AI Engineer
As artificial intelligence continues to transform industries, AI Engineers play a critical role in designing and deploying AI-driven solutions that enable businesses to automate processes and make smarter decisions. These professionals combine software engineering, machine learning, and data science to build intelligent applications and services used across various sectors.
On a typical day, an AI Engineer might develop new machine learning models, optimize existing algorithms for better accuracy, and deploy AI solutions into production environments. They frequently collaborate with software developers, data scientists, and product teams to ensure AI systems integrate seamlessly with existing workflows, providing meaningful improvements to business performance.
Salary: \$161K–\$267K/yr
Responsibilities:
- Design and implement machine learning models and generative AI systems.
- Optimize and refine AI algorithms for real-world applications.
- Develop APIs and integrate AI solutions into existing software platforms.
- Evaluate model performance and make iterative improvements based on data-driven feedback.
- Collaborate cross-functionally to deliver AI-driven projects aligned with strategic goals.
Key Skills:
- Advanced proficiency in programming languages such as Python, Java, or C++.
- Expertise in machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
- Strong mathematical foundation in statistics, calculus, and linear algebra.
- Ability to deploy and manage machine learning models in cloud environments (AWS, Azure, or GCP).
- Excellent problem-solving and analytical thinking skills for complex technical challenges.
- Strong communication skills for collaborating with cross-functional teams and stakeholders.
As AI continues its rapid expansion into industries ranging from technology and finance to healthcare and retail, AI Engineers will play a central role in developing the smart tools and systems shaping our digital future. Their specialized knowledge and innovative work are essential for harnessing the full potential of artificial intelligence.
How to Prepare for These Roles
Want to excel in data science? Focus on three key areas: technical skills, practical projects, and continuous learning. Here's how to set yourself up for success in this exciting field.
A: Master Essential Technical Skills
First, become proficient in programming languages commonly used in data science, such as Python and R. Next, learn how to clean data, create visualizations, and implement machine learning algorithms. Developing these abilities will allow you to tackle complex datasets and perform the advanced analyses required in data science roles.
B: Showcase Your Skills Through Projects
One of the best ways to demonstrate your capabilities to potential employers is by building an impressive portfolio. Look for opportunities to take on personal projects where you analyze real-world datasets. You can also contribute to open-source initiatives. This hands-on experience not only hones your skills but also highlights your ability to apply theoretical knowledge in practice
C: Commit to Lifelong Learning
Data science is a rapidly evolving field, so staying up-to-date is essential. Engage with professional communities, attend relevant conferences, and tap into online learning resources. These activities will give you valuable insights into current industry practices and future directions. Remember, continuous skill development is key to thriving in data science.
In summary, preparing for a data science career involves a well-rounded approach. By mastering technical skills, applying them through practical projects, and embracing lifelong learning, you'll be well-equipped for success. As data science continues to advance, these strategies will help you thrive both now and in the future.
How to Choose the Best Data Science Role for You
Choosing the best data science job comes down to knowing your strengths, skills, and what each job requires. This section will walk you through a self-assessment to help figure out which position might be your ideal match.
The Different Data Science Roles
Data science includes several distinct roles, each with its own set of responsibilities and necessary skills:
- Data Engineer: Builds infrastructure and pipelines for collecting, storing, and processing data.
- Data Scientist: Examines complex data to uncover insights, make predictions, and develop strategies.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Creates algorithms and predictive models using big data.
- Data Architect: Designs the blueprints for an organization's data management systems.
Assessing Your Fit for a Data Science Career
To determine if a data science career is right for you, ask yourself:
- Are you passionate about continuous learning and problem-solving?
- Do you feel comfortable with programming languages and data analysis tools?
- Can you effectively communicate complex data insights?
- Are you persistent enough to tackle difficult data challenges?
- How well do you collaborate on projects with different teams?
Your answers to these questions can provide valuable insight into which data science role best aligns with your abilities and interests. Top data scientists have a blend of technical skills, analytical capabilities, and personal qualities like curiosity and a keen eye for detail. Specialized machine learning skills are also predicted to be in high demand for these positions.
Aligning Your Career for Satisfaction
It's crucial to match your personal traits with your professional goals. Making sure your abilities fit the requirements of a specific role not only boosts job satisfaction but also enables career growth. So whether you're a student hoping to enter the field or a professional looking to advance, understanding these alignments is key.
In summary, taking time to reflect on your strengths and objectives can significantly help in identifying the data science role that's the right fit for you. Choosing a career path well-suited to your skills and interests will put you on the road to success and fulfillment in this exciting field.
At the End of the Day...
Data science roles are shaping the future of business and technology. In this article, we explored 10 high-demand data science jobs that are making a big impact. From data engineers to AI ethics officers, these positions offer diverse and rewarding career paths.

If you're ready to launch your data science career, a strong educational foundation is key. Here's how to get started:
Kickstart Your Data Science Career
- Begin your journey with Dataquest's Data Scientist in Python career path
- Dive deeper into cutting-edge techniques with the Machine Learning in Python skill path
- Apply your skills to real-world data science projects to showcase your expertise to employers
As data science continues to evolve, adaptability and continuous learning are essential for staying competitive. By honing your skills with Dataquest's interactive courses and hands-on projects, you'll be well-prepared to thrive in the exciting world of data science.
from Dataquest https://ift.tt/Uk0uwz8
via RiYo Analytics

No comments